Building a Demand Forecasting Platform at Fortune 500 Scale using Azure Databricks and FastAPI
When a Fortune 500 CPG giant needed to accurately predict product demand during high-stakes promotional events like Diwali, festive seasons, and major sales campaigns, our team was brought in to build a production-grade ML platform that could handle the complexity of promotional forecasting. This case study explores how we designed and deployed an enterprise demand forecasting solution on Azure that transformed promotional planning from guesswork into data-driven strategy, enabling better inventory management and revenue optimization during critical sales periods.
The Challenge
For consumer goods companies promotional events and festive seasons represent massive revenue opportunities but also significant risk. Poor demand forecasts during these periods can lead to millions in lost sales from stockouts or costly excess inventory. The challenges we needed to address included:
- Promotional complexity: Demand during offers and festive periods doesn’t follow normal patterns, discounts, bundles, and marketing campaigns create unpredictable spikes
- Event diversity: Different festivals (Diwali, Holi, Eid, Christmas) and promotional types (percentage discounts, buy-one-get-one, combo offers) each impact demand differently
- Lead time pressure: Forecasts needed weeks in advance to coordinate manufacturing, distribution, and retail partnerships, but promotional details often finalized late
- Product interdependencies: Promotional bundles and cross-selling effects meant forecasting couldn’t happen in isolation for each SKU
- Scale and speed: Generating forecasts for thousands of SKUs across multiple promotional scenarios in time for planning cycles
The client needed a demand forecasting platform that could capture the unique dynamics of promotional demand while remaining flexible enough to handle the constant evolution of marketing strategies.
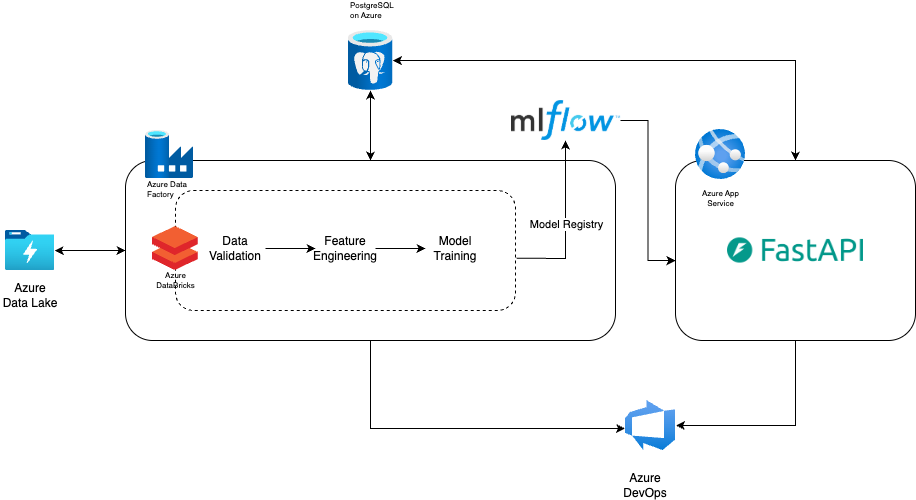
Solution Architecture
We designed a cloud-native platform on Azure with these core components:
- Data Processing Layer: Azure Databricks for scalable feature engineering from historical promotions and sales data
- Orchestration: Azure Data Factory to coordinate multi-stage data pipelines
- API Layer: FastAPI-based microservices deployed on Azure App Service for scenario planning and real-time forecast generation
- Model Management: MLflow model registry for versioning and deployment, with ensemble forecasting combining CatBoost, LightGBM, and statistical models
- CI/CD Infrastructure: Azure DevOps pipelines for automated testing and deployment
Implementation
As the MLOps engineer on this project, my role was to take the forecasting models developed by our data science team and build the production infrastructure around them. I focused on translating experimental notebooks into scalable data pipelines, creating API interfaces for model serving, and establishing automated deployment workflows, essentially bridging the gap between data science experimentation and production-ready systems.
Machine Learning Pipelines
Working closely with the data science team, I translated their feature engineering logic from exploratory notebooks into production-ready PySpark pipelines. The data scientists had identified key promotional features: discount depth, festival timing, historical performance, and cross-promotional effects. My responsibility was building robust Databricks jobs that could:
- Process years of promotional history efficiently across the full product catalog
- Ensure consistency between training and inference feature generation
- Implement data quality checks and monitoring at each pipeline stage
I established validation checkpoints throughout the pipeline, ensuring the features flowing to models matched what data scientists expected during experimentation.
Model Deployment and Serving
The data science team came up with an ensemble approach combining CatBoost, LightGBM, and statistical models, each optimized for different aspects of promotional demand. My focus was operationalizing these models:
Production deployment:
- Built model loading and inference wrappers that handled the ensemble logic
- Implemented preprocessing pipelines that exactly replicated training transformations
Performance optimization:
- Profiled inference latency and optimized bottlenecks
- Implemented caching for frequently computed features
- Enabled efficient batch predictions for multi-SKU forecasts
The critical challenge was ensuring production inference exactly matched the data scientists’ expectations any feature calculation discrepancy would degrade accuracy.
FastAPI for Promotional Scenario Planning
The API layer needed to support more than just batch forecasting, planning teams needed to explore different promotional strategies interactively, to handle this I designed async endpoints that could process multiple promotional scenarios concurrently. Planning teams could submit requests like “forecast Diwali demand with 25% discount vs. 35% discount vs. bundle offer” and receive comparative forecasts rapidly.
Endpoints also supported various views, SKU-level, category-level, regional rollups allowing different stakeholders to access forecasts at their required granularity. This API-first approach transformed promotional planning from a slow, batch-oriented process into an interactive, data-driven activity.
Azure Data Factory: Workflow Orchestration
I designed Data Factory pipelines to automate the forecasting workflow:
- Automated retraining: Models retrained after major promotional events to incorporate latest performance data
- Data integration: Coordinated pulling promotional calendars, marketing plans, and historical data from various sources
- Pre-event preparation: Generated baseline forecasts for upcoming festivals, giving planning teams a head start
CI/CD with Azure DevOps
We designed comprehensive deployment pipelines that enabled:
- Automated testing: Unit tests for data processing, integration tests for APIs, and model performance validation
- Environment management: Separate dev, staging, and production environments
- Quick deployment: Enabled data scientists to trigger model updates through pull requests with automated validation
During critical pre-festival planning periods, this infrastructure allowed us to quickly deploy improvements and incorporate late-breaking data.
Results and Impact
The platform delivered tangible improvements in promotional planning and execution:
-
Improved forecast accuracy: Promotional period forecast accuracy improved significantly compared to previous methods, particularly for major festivals where historical patterns provided strong signals
-
Faster planning cycles: What previously took days of manual analysis and spreadsheet modeling now happened in minutes through the API, enabling teams to explore more promotional strategies
-
Better inventory positioning: More accurate demand forecasts enabled smarter inventory decisions, reducing both stockouts during hot-selling promotions and excess inventory after events
-
Scenario planning capability: Planning teams could now quantify the demand impact of different promotional strategies before committing resources, leading to more optimized promotional calendars
Key Learnings
1. Promotional forecasting is fundamentally different from base demand forecasting
Standard time-series models struggle with the discontinuities that promotions create. Success required purpose-built features and models that explicitly captured promotional mechanics rather than treating them as noise to smooth over.
2. Feature engineering matters more than model choice
The difference between a mediocre and excellent promotional forecast came down to how well features captured promotional contextdiscount depth, festival timing, competitive activity, and historical comparable events. I learned to invest heavily in feature quality.
3. Speed enables better planning
The API-driven architecture changed how teams worked. Being able to instantly compare promotional scenarios meant planning teams could be more creative and data-driven in their strategies.
4. Collaboration between MLOps and data science requires clear interfaces
Regular communication with the data science team was essential. We established shared conventions for feature names, model artifacts, and expected input/output formats. When data scientists needed to experiment with new features, we worked together to ensure they could be efficiently computed in production. This collaboration prevented the common pitfall of models that work great in notebooks but fail in production.
Tech Stack
- Backend & APIs: Python, FastAPI, Pydantic
- ML & Data Processing: PySpark, CatBoost, LightGBM, statsmodels, pandas, NumPy
- Infrastructure: Docker, Azure AppService, Azure Databricks, Azure Data Factory
- CI/CD: Azure DevOps Pipelines
- Monitoring: Azure Monitor, Application Insights
Conclusion
This project reinforced that production ML success comes from reliable infrastructure and cross-functional collaboration. Most importantly, the platform transformed how planning teams worked. What previously took days of manual analysis now happened in minutes, enabling teams to explore promotional strategies confidently with data rather than intuition. That business impact validated the engineering investment: a good machine learning system doesn’t just serve predictions, it changes how organizations make decisions.